Lesson 1: The Editor Window#
Let us have a closer look at the Editor Window.
Syntax Highlighting#
Upon finishing the final character in a class name (e.g., AnySeg), the font will turn blue. This is a good way to check for spelling errors. For example,
AnySeg
The editor similarly recognizes comments. If you precede the AnySeg class name with a double-slash, the entire line turns green, and AnyBody will ignore the line when loading the model:
// AnySeg
You can turn entire blocks of code into a comment by encapsulating it in
a pair of /* */ delimiters. You can also comment and un-comment
several lines by highlighting the block of lines and using the two
buttons  in
the toolbar. This automatically places or removes double slashes in front of
each line in the block.
in
the toolbar. This automatically places or removes double slashes in front of
each line in the block.
Please also notice the so-called Documentation Comments. These are
comments using the following syntactical forms: /// ... ,
/** ... */ , ///< ... , and /**< ... */.
The Documentation Comments are related to
a given object in the model, and these comments are treated specially so
the information can be accessed more conveniently after loading the
model. Documentation comments appear in the object descriptions of the
model; it makes it easier to understand a model just by browsing the
Model Tree.
Auto-indent#
Consistent indentation of the text in your scripts makes your code easy to read. In AnyScript it also makes it simpler to maintain an overview of start and end braces for a section.
You can auto-indent a block of code in one simple step by highlighting
the block and pressing Alt+F8. This can also be done through the
pull-down menu Edit->Format Indentation or by the  button in the toolbar.
button in the toolbar.
If you are ever in a situation where the model will not load, and you suspect that you have forgotten a brace somewhere, simply highlight the entire file and apply Auto format to it. You should be able to spot the error soon.
Tree Views#
The structure of an AnyScript model is hierarchical, which allows AnyBody to represent the loaded model as a tree.
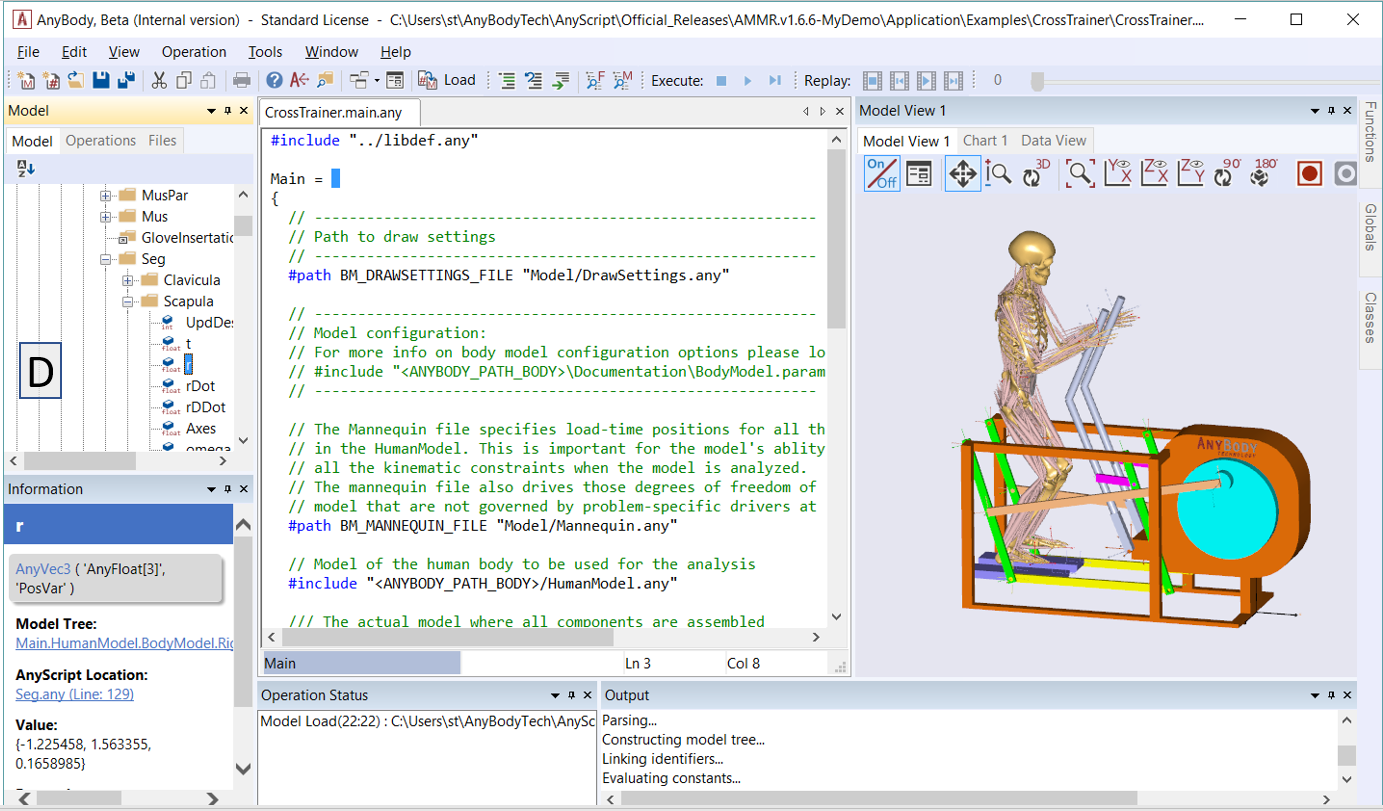
What you see here is the Model Tree (D), which shows all objects in the loaded model, in the same organizational structure that is defined by the AnyScript code.
Right-clicking on an object in the Model Tree gives you access to many functions, the most important of which are:
Inserting Object Name at cursor location in the AnyScript text editor.
Locating all references to an object in AnyScript
Class Operations (example: Saving an STL file)
Control object display in the Model View
Getting an object description
The Object Description contains useful links which for instance, take you the object’s creation point in AnyScript with a single click. You can also open the Object Description by double-clicking any node in the tree.
The information window (G) provides a condensed version of the Object Description. Please refer to the introductory video found here for more Model Tree navigation features.
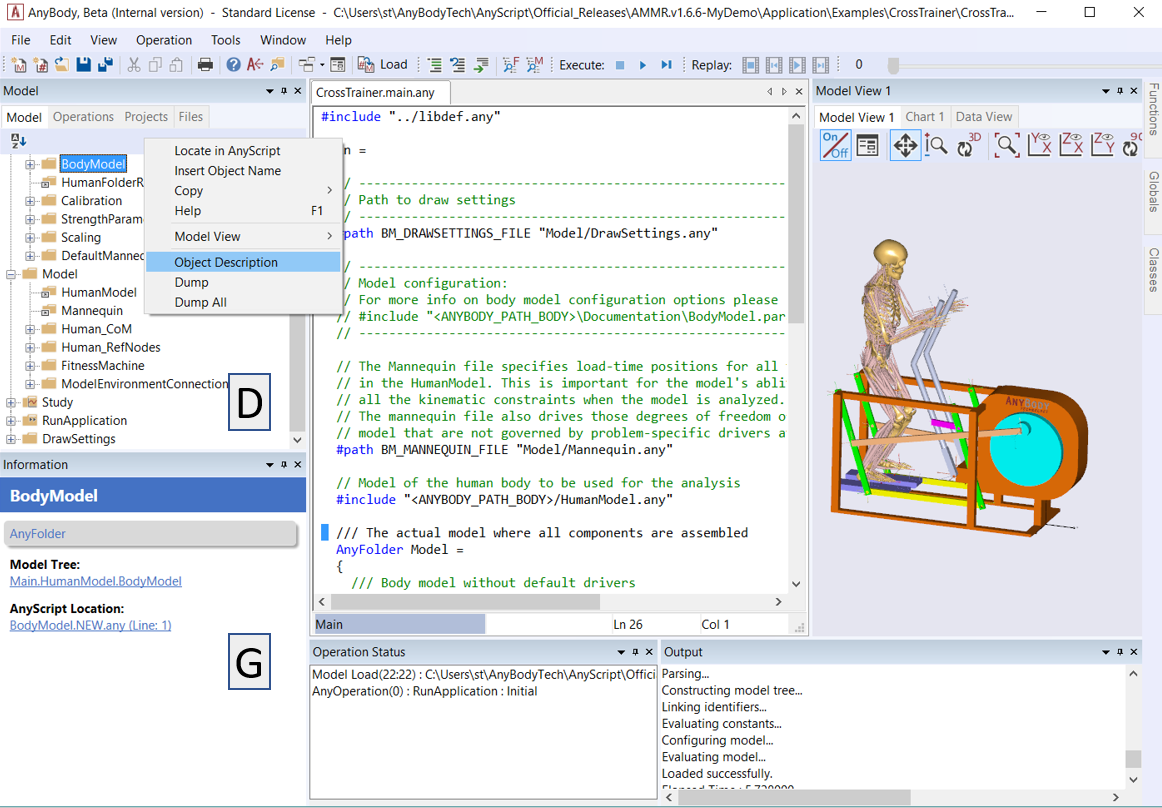
The Files tab (in the same window as the Model Tree) gives an overview of the ‘.any’ files used to define the current model. Double-click on file names to navigate to the #include AnyScript statements that link them to the parent file. Below you see the File Tree from the CrossTrainer model:
One the right side of AnyBody there are three tabs, Functions, Globals and Classes. These tools speed up your AnyScript experience. For example, Classes gives you access to a list of the predefined classes in the system - which are essentially templates for defining model objects having specific functions.
If you are unsure on how to write the code for an object of a certain class, first position your cursor appropriately in the AnyScript Window. Then right click on a class name from the list and select “Insert Class Template” (see image below). Remember to replace any placeholder text in the inserted template as required. Read more from Getting Started:AnyScript Programming tutorial.
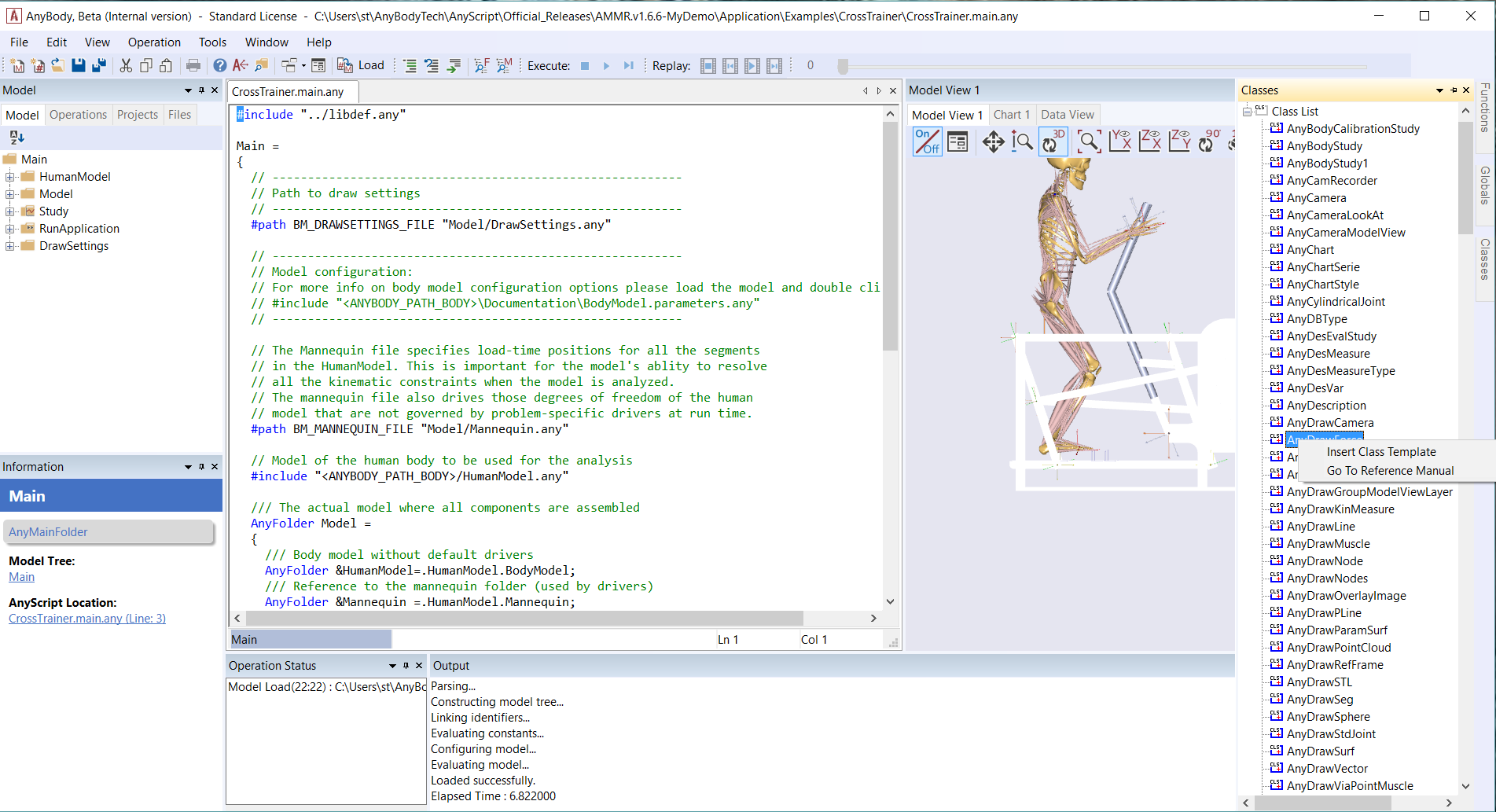
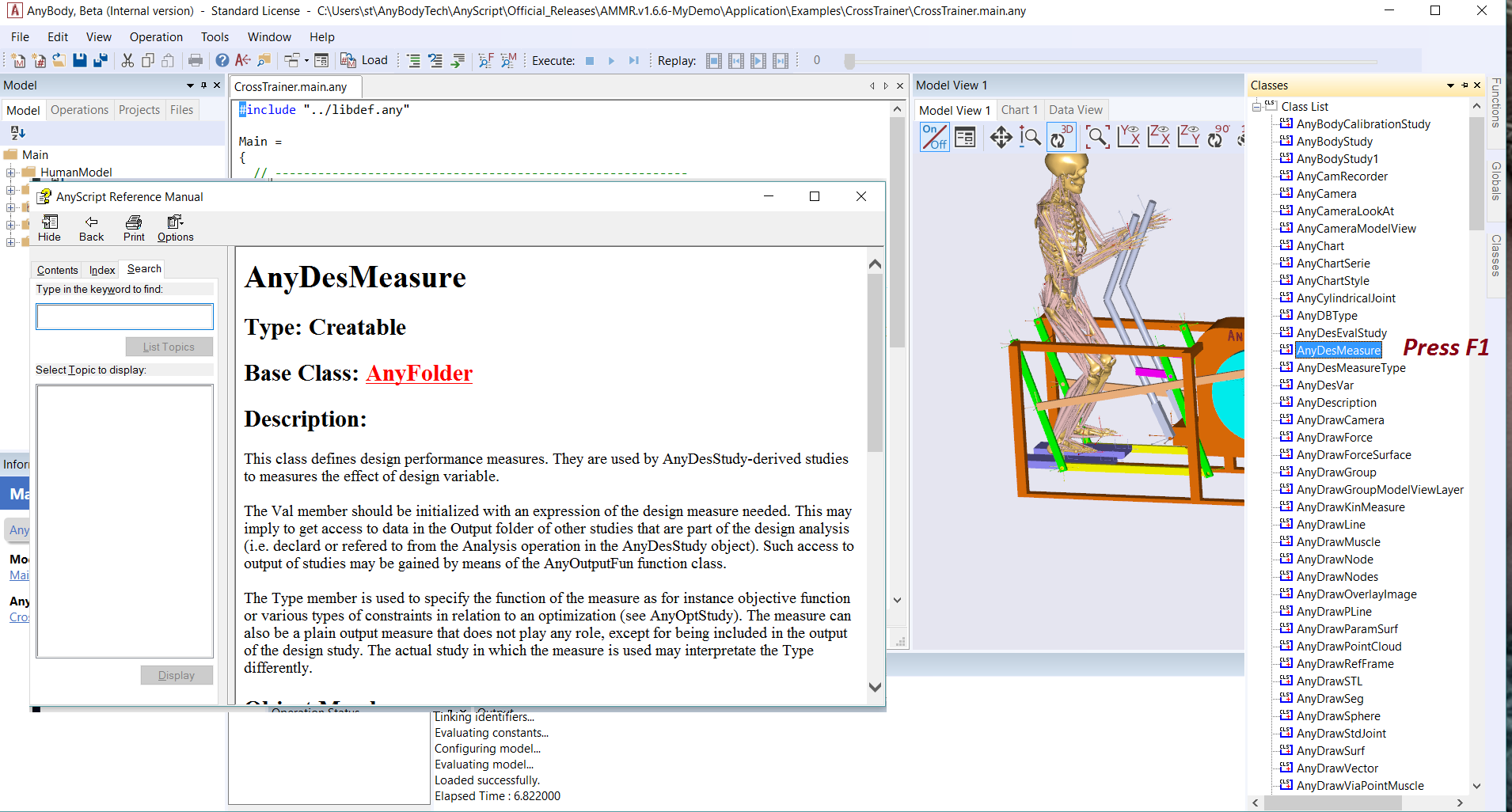
Similarly, the Functions tab gives you a list of inbuilt functions and the arguments that they accept. You can learn more about each class or function by clicking on its name in the list and pressing the F1 key, which takes you to the AnyScript reference manual (see image below).
Note
Scrolling to the bottom of the object description in the reference manual you will typical find small example models which show the usage of that class or function.
Find and Replace#
Find and Replace functions are available in the Edit menu. Alternatively, you can use:
Ctrl+F for find. Ctrl+H for find and replace.
F3 repeats the previous find operation.
Support for External Editors#
Some users have strong preferences when it comes to editors. The AnyBody Modeling System allows you to use any text editor like Notepad++ to author your models, as long as it saves the files in an ASCII text format. Please refer to the Wiki at anyscript.org for more details.